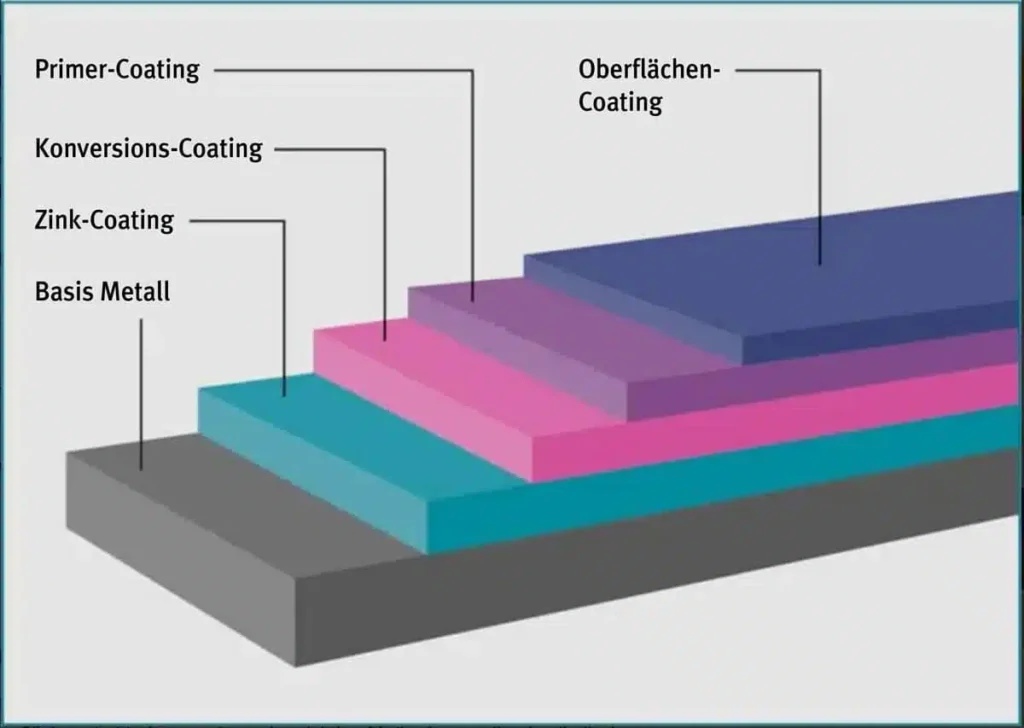
What are coatings?
The term “coatings” refers to vehicle, car repair and industrial paints as well as all types of architectural coatings.
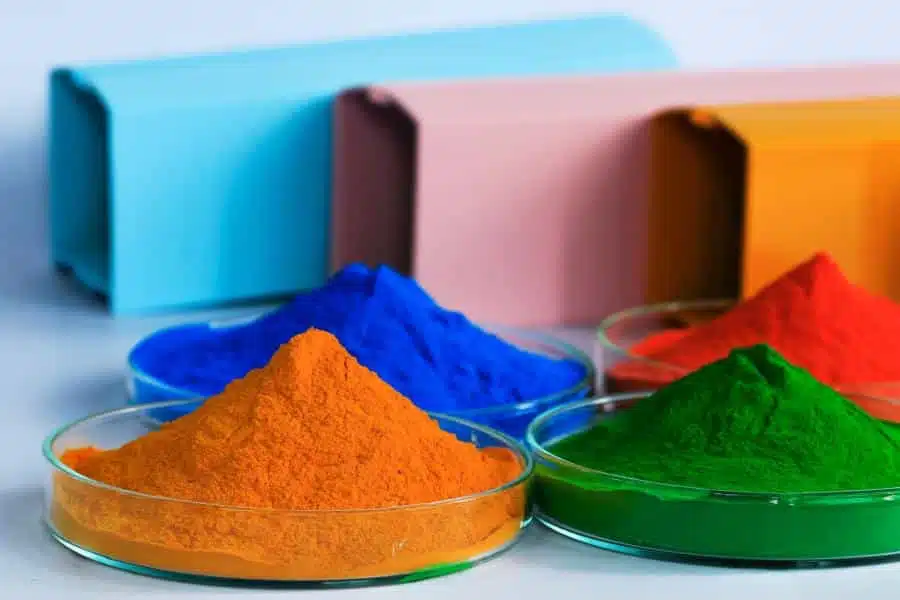
When it comes to coatings, we pay particular attention to sustainability. Integrated exhaust air filter systems capture the aspiration dust generated during the mixing process, thus minimizing product loss of the bulk material and environmental pollution. In manufacturing technology, coating is the process of applying a firmly adhering layer of shapeless material to the surface of a workpiece. The corresponding process and the applied layer itself are also referred to as coating. The coating can be a thin layer or a thick layer or several contiguous layers.
Coating processes can be differentiated according to:
- the initial condition of the material to be applied
- the type of carrier material (substrate)
- the type of adhesion promoter (primer)
Application
In addition to alloying, doping and surface structuring, coating is a very important method of influencing the physical, electrical and/or chemical properties of metallic or semi-metallic materials.
Properties and measurability
- Adhesion:
Using the cross-cut test (in accordance with ISO 2409), the coating is scored crosswise and thus divided into a checkerboard pattern. By applying and removing an adhesive tape, the number of paint pieces still adhering is compared with the pieces that have stuck to the adhesive tape and a result is obtained. - Coating thickness:
There are a variety of measurement techniques in process engineering for determining coating thickness. In ellipsometry, polarized light is used to determine the change in the polarization state of light when a sample is reflected, thus determining the thickness. - Corrosion resistance:
Protection against corrosion is very important and therefore metals are subjected to many tests to ensure a perfect result for the customer. Spray tests can test the susceptibility to corrosion by salts. In climate tests, the test objects are exposed to changing temperatures and humidity in a climate chamber. Resistance to UV radiation can be tested in special irradiation chambers, some of which also simulate weathering (e.g. rain).