What is a suspension?
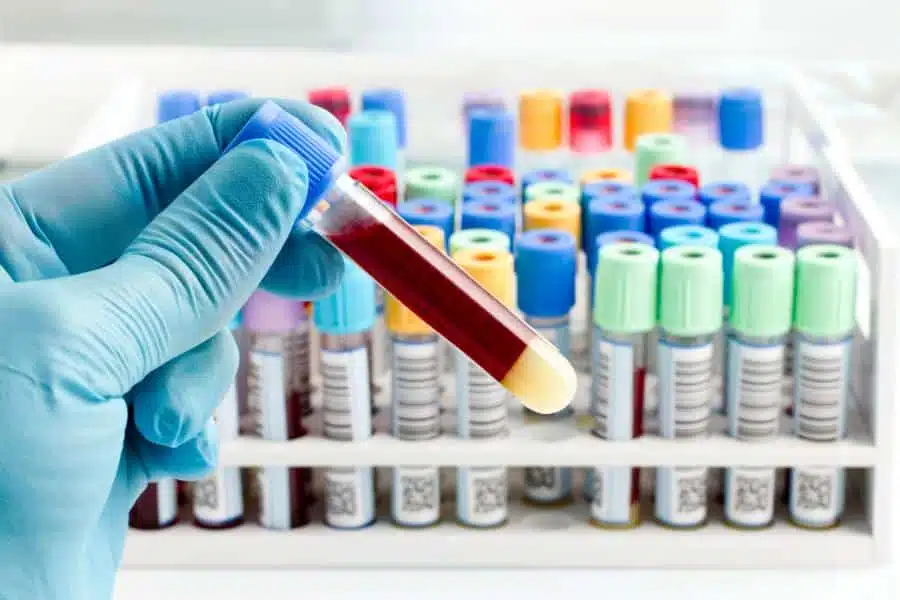
A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture of a liquid and a solid substance dispersed in it. In polymer chemistry, suspensions or dispersions are finely dispersed polymer products that are obtained by suspension polymerization.
Examples of suspensions
- Slurries of sand in seawater
- Mortar or concrete (mineral suspensions)
- Covering paint or coating
- The body’s own blood
- Wheat beer or orange juice
Sedimentation
Sedimentation describes the deposition of particles from liquids or gases under the influence of gravity. If a suspension is left to stand for a longer period of time, the solid sinks to the bottom and forms a sediment. The smaller the particles of the solid, the lower its density and the higher the viscosity of the liquid, the slower the sedimentation process. Sedimentation can be accelerated using centrifuges.
Viscosity
The term is a measure of the viscosity of a suspension. The opposite describes the fluidity, a measure of the flowability. The higher the viscosity, the thicker the fluid; the lower the viscosity, the thinner the fluid and the faster it can flow.
Online sources:
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Suspension_%28Chemie%29, retrieved: September 28, 2019, 10:40 UTC