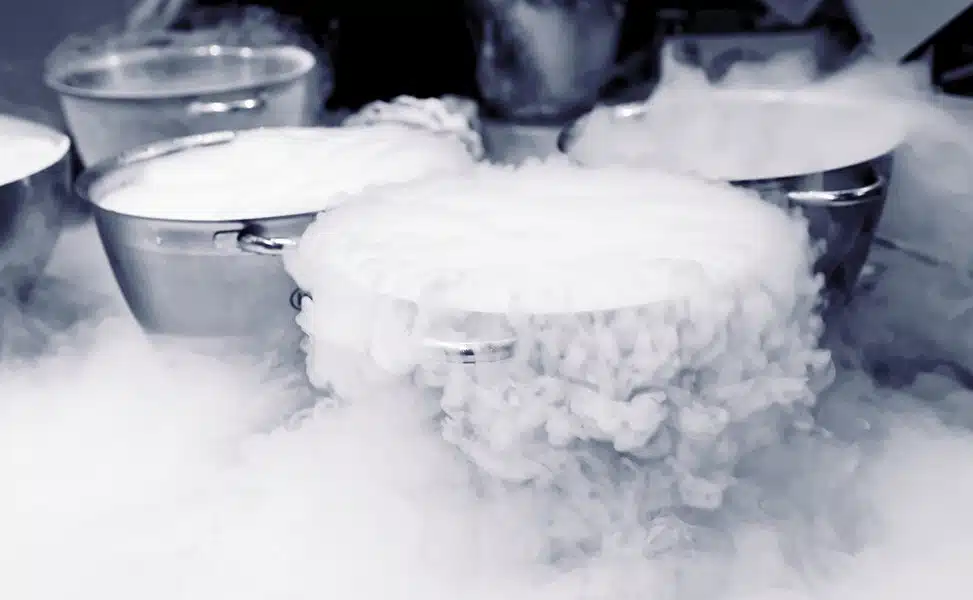
What is cold grinding or cryogenic grinding?
Cold grinding – also known as cryogenic grinding or cryogenic milling – describes the process in which liquid nitrogen is added to the materials to be ground in order to obtain particularly high particle sizes with consistent quality during micronization. This process of ultra-fine grinding (cryogenic grinding) is mainly used for soft, flexible or moist materials, as these are often difficult or impossible to grind. As soon as the ground material is cooled, the material properties change during cold grinding: The material becomes hard and brittle – thus enabling the finest grinding processes. This prevents the ground material from melting and sticking together during micronization. In the case of spices, the aroma and flavors can be lost due to the high temperatures generated by the grinding energy. There is also a risk of oxidation and even dust explosion.
Cold grinding is suitable for many materials, for example:
- Thermoplastics
- Rubber / elastomers
- Grow
- Spices
- Pharmaceuticals
The advantages of cold grinding (cryogenic grinding) at a glance:
- High throughput of ground material
- Large proportion of fine or ultra-fine material
- Lower specific energy requirement
- No melting and bonding of temperature-sensitive plastics
- No thermal damage due to a controlled grinding temperature
- Preservation of aromatic substances during spice grinding
- High protection against dust explosions
Cold grinding is carried out at Ebbecke Verfahrenstechnik AG using the Cryogenic Mill. It is therefore also referred to as cryogenic grinding or cryogenic milling.