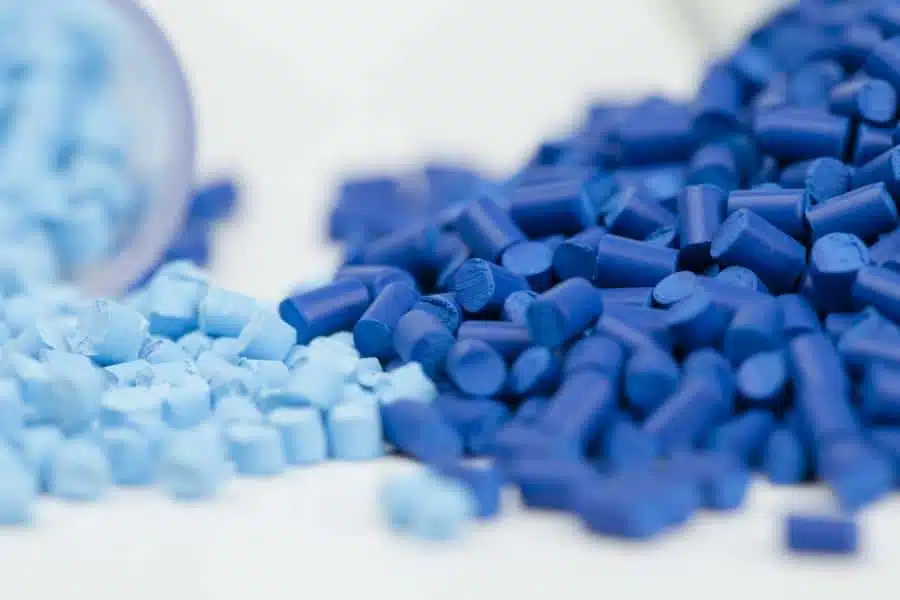
What are granules?
The term granulate comes from the Latin “granum” – grain and refers to small granular or spherical solids that appear together as granular matter. Sand, for example, is a granulate consisting of many individual grains.
In principle, granulates can be based on very different materials such as plastics, metals, minerals, wood or other organic or inorganic materials. In addition to granular variants, there are also powdery granulates such as powder or, in very large quantities, loose materials such as rock debris.
In industry and logistics, the term bulk goods is often used in this context.
How are granules produced?
In addition to naturally occurring granulates such as sand, granulates are also produced industrially for a wide range of applications, e.g. by grinding, milling or crushing larger materials.
A distinction is made between two types of granules: build-up and degradation granules. In the production of build-up granulates, techniques such as pelletization, boiler granulation or fluidized bed processes are used. For degradation granulates, a distinction is made between wet and dry granulates. In wet granulation, the powder is processed into a dough with the addition of a granulating liquid and pressed into perforated disks. Alternatively, the powder can be dried, pressed into briquettes and then ground. Classification produces a granulate with a uniform particle size (dry granulation).
Granules increase flowability and adhesion when compressed into tablets. They are generally more uniform than powders and therefore enable a more even tablet mass and better dosing accuracy.
Areas of application for granules
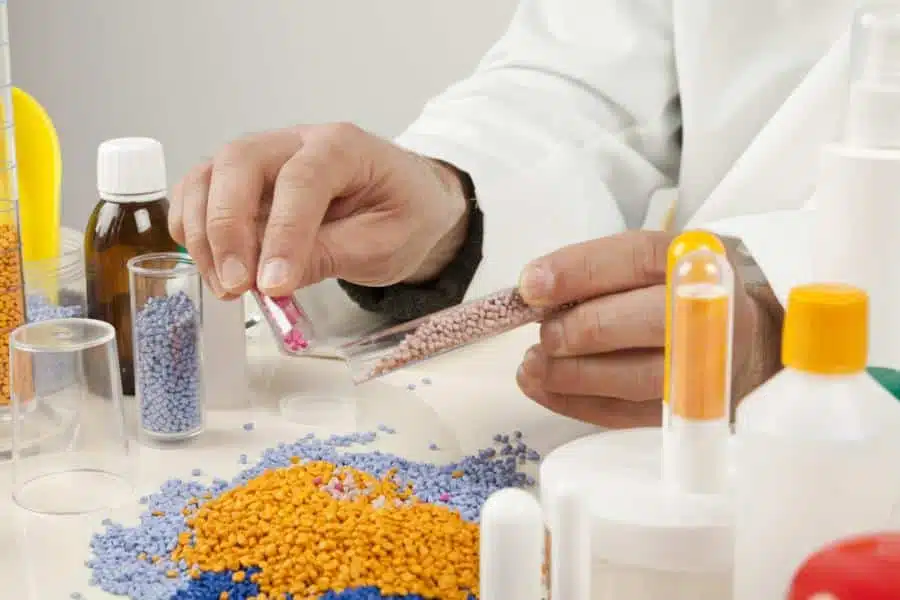
Granules are used in a variety of applications, such as in the plastics industry for the production of plastic parts, as fillers in concrete, as fertilizers in agriculture, as catalysts in chemical reactions and as carrier materials in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries. Due to their granular structure, granules can be easily stored, transported and dosed, making them a versatile material.
- Plastics industry: Granulates are often used as a starting material for the production of plastic parts. The use of granulates enables plastic parts to be produced quickly and efficiently.
- Agriculture: Fertilizers in granular form are used to improve soil quality and promote plant growth. They can also be used as carrier materials for pesticides or other agricultural chemicals.
- Construction industry: Granulates are used as fillers in concrete, asphalt and other building materials to improve the strength and durability of the materials.
- Chemical industry: In the chemical industry, granulates are used as catalysts or as carrier materials for chemical reactions.
- Pharmaceutical and cosmetics industry: Granules are used here as carrier materials for drugs and cosmetics to distribute the active ingredients evenly and facilitate dosing.
- Food industry: Granules can be used as ingredients in food production, for example as binding agents or texturizing agents.
- Environmental technology: Granulates are used in waste disposal and processing to bind or filter waste.
Granulate: Compacting at Ebbecke Verfahrenstechnik
A. Ebbecke Verfahrenstechnik AG offers its customers the option of compacting raw materials into pellets.
Applications in which the compaction of granulates can be advantageous:
- Transport: Compacting granulates can reduce the volume, which makes it easier to transport materials. For example, larger quantities of granulates can be transported in a single truck.
- Storage: Compacting can make granulates more stable and resistant to external influences such as moisture or humidity, which facilitates storage and increases the shelf life of the materials.
- Processing: Compacted granules can be used as starting materials in various industrial processes such as the production of plastic parts or concrete. The higher density and strength of the granules can help to improve the quality of the end products.
- Dosing: In some applications, it is important that granules are dosed in specific quantities, for example in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals or in the food industry. Here, compacted granules can help to precisely control the dosage and improve the distribution of the materials.
- Recycling: Compacted granulates can also be beneficial when recycling materials. For example, they can be reused as raw materials for the manufacture of new plastic parts or other products.
Overall, compacting granules can help to improve their handling and use in various applications and increase their versatility as a material.
Online source:
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulare_Materie, retrieved: May 4, 2023, 10:45 UTC
Literature source:
The processing stages of plastic, from granulate to finished product: the business aspects that need to be taken into account in market research and sales / Beat Halter / 1962