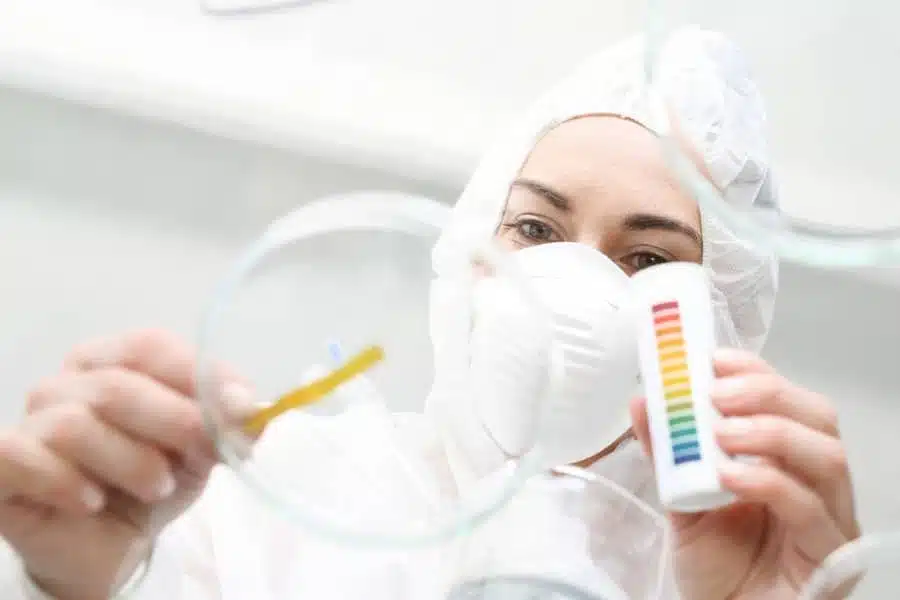
What is the pH value?
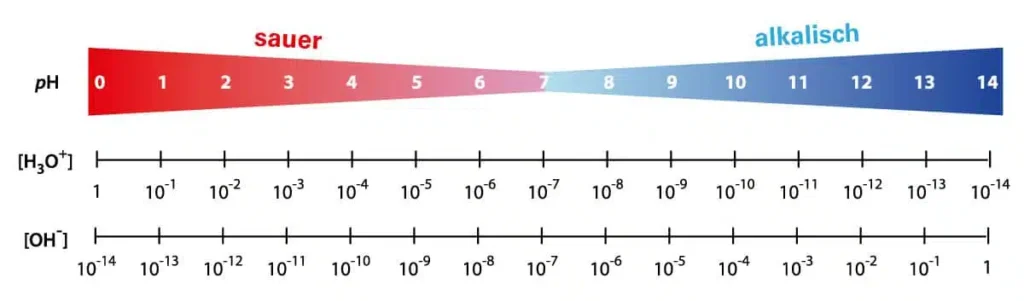
The pH value is a measure of the strength of the acidic or alkaline effect of an aqueous solution. The term is derived from “pondus Hydrogenii” or “potentia Hydrogenii” (Latin pondus, n. = weight; potentia, f. = power; hydrogenium, n. = hydrogen).
The classification for pure water and diluted solutions at 25 °C:
- pH < 7 corresponds to a solution with an acidic effect
- pH = 7 corresponds to a neutral solution
- pH > 7 corresponds to an alkaline solution (alkaline effect)
The pH value can be determined very easily and quickly in everyday clinical practice using a blood gas analysis (BGA). This is also extremely important in emergency medicine, as the pH value of the blood often serves as an important indicator of certain diseases or disorders. The first thing the doctor looks at is whether the pH value is higher or lower than in healthy people.
- If the pH value in the blood falls below 7.37, acidosis is present.
- If the pH value rises to 7.45 or higher, doctors speak of alkalosis.
In the Ebbecke Verfahrenstechnik AG laboratory, precise determination of the pH value is important for many containers. In addition to determining the water content and moisture and analyzing the grain size, the team defines the grain shape, creates microscopic images and determines the bulk density, tapped density or annealing residues.