What is an emulsion? The definition
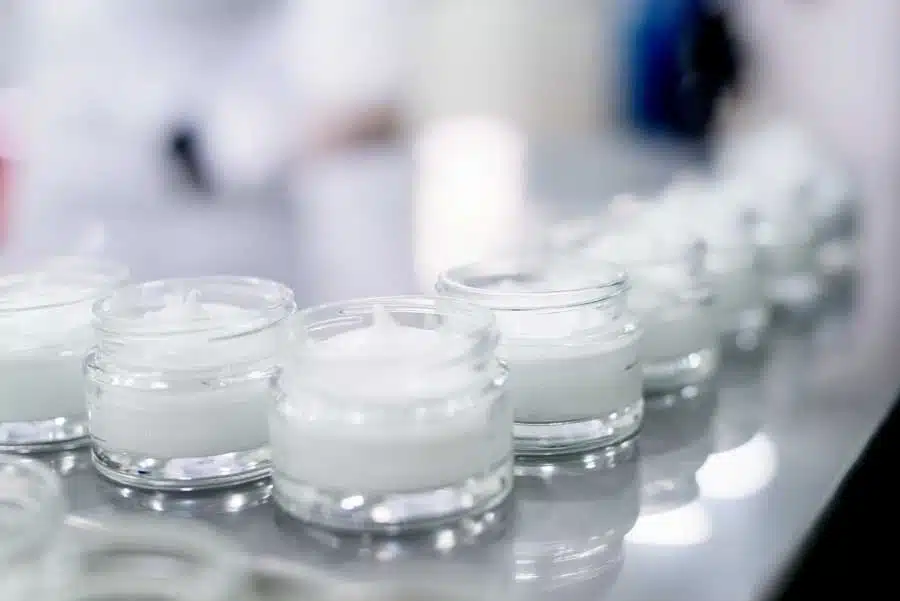
An emulsion is a finely dispersed mixture of two normally immiscible liquids without visible separation. Examples of emulsions are numerous cosmetics, milk or mayonnaise.
Structure of the emulsion
An emulsion is a finely dispersed mixture of two liquids, such as oil and water. One liquid (phase) forms small droplets distributed in the other liquid. The phase that forms droplets is called the inner phase or disperse phase. The phase in which the droplets float is called the outer phase or continuous phase. Emulsions belong to the disperse systems and differ from mixtures of miscible liquids, such as ethanol and water. Emulsions are usually cloudy, milky liquids.
Emulsions made of water and oil are divided into water-in-oil emulsion (W/O emulsion) and oil-in-water emulsion (O/W emulsion). Another important component of emulsions is the emulsifier (surfactant), which facilitates the formation of droplets and counteracts segregation (phase separation).
Online source:
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emulsion, retrieved: March 11, 2020 15:54 UTC