What is infrared radiation?
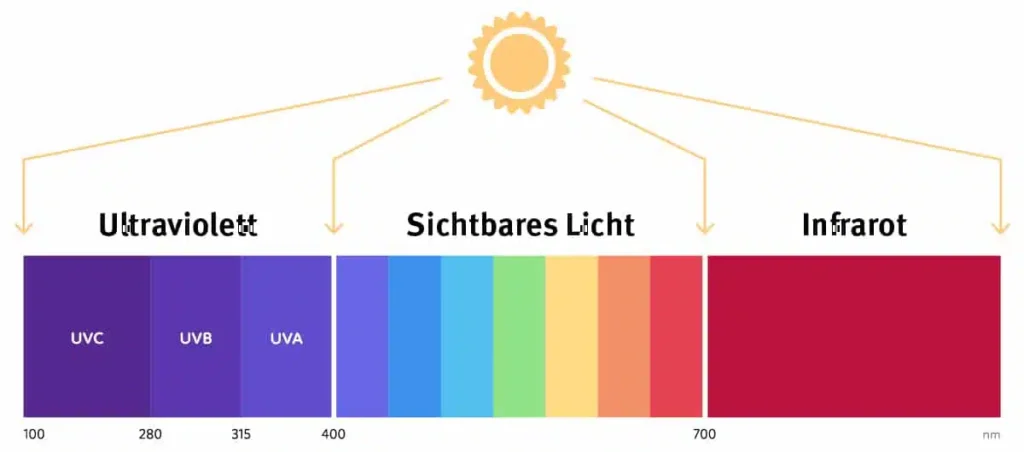
Infrared radiation, also known as thermal radiation, is part of optical radiation and therefore part of the electromagnetic spectrum. It joins visible light in the direction of longer wavelengths. The most important natural source of infrared radiation is the sun. Infrared radiation accounts for 50 percent of the solar radiation that reaches the ground. In addition, the earth warmed by solar radiation emits infrared radiation.
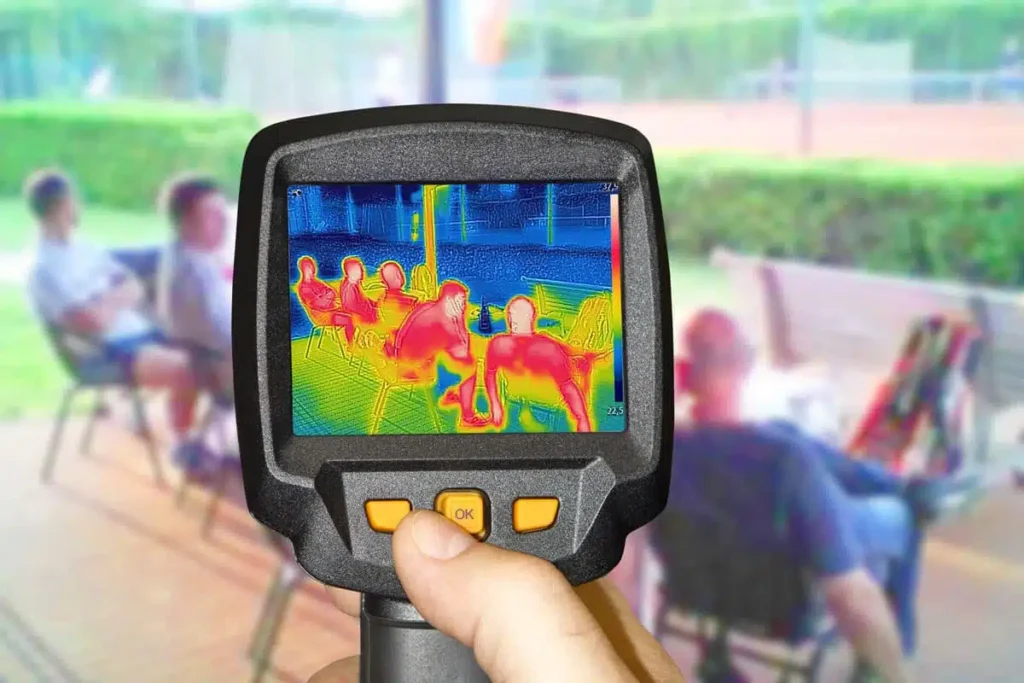
We ourselves experience infrared radiation every day. The warmth we feel in sunlight or in front of a fire, a radiator or a hot asphalt surface is infrared radiation. Even if our eyes cannot see it, the nerves in our skin perceive it as heat.
Infrared radiation can be divided into three main categories:
- Near infrared (NIR): This region is close to the visible light spectrum and has shorter wavelengths. It is often used in technologies such as remote controls, optical communication systems and near-infrared spectroscopy devices.
- Mid-infrared (MIR): This range includes longer wavelengths and is often used in applications such as thermal imaging cameras, sensor technology and industrial processes for temperature monitoring.
- Far infrared (FIR): This range has the longest wavelengths and is mainly used for therapeutic and wellness applications, such as infrared saunas or heat therapy devices.
Infrared radiation interacts with matter in different ways. It can be reflected, absorbed or transmitted by surfaces, depending on the properties of the material. Therefore, infrared radiation is used in various fields such as physics, chemistry, medicine, communication and industry.
Infrared radiation is also important in environmental science. It makes it possible to study the heat distribution and radiation of the earth’s surfaces, atmosphere and oceans, which is of great importance for research into the climate and climate change.
What role does infrared radiation play in process engineering?
Infrared radiation plays an important role in process engineering, especially in areas that have to do with heat transfer, drying, heating and thermal processes:
- Drying: Infrared heaters are often used in drying systems to remove moisture from materials. The infrared radiation heats the material, causing the bound water to evaporate. This process is widely used in sectors such as food processing, paper manufacturing and the textile industry.
- Heating: Infrared heaters are used to heat materials quickly and evenly. This is particularly useful in plastics processing, where plastics need to be melted, or in the manufacture of glass or metal, where precise and efficient heating is required.
- Heat curing: In process engineering, infrared radiation is often used to cure coatings, paints or adhesives by applying heat. This enables faster curing compared to conventional methods and offers a higher production speed.
- Surface treatment: Infrared radiation is used to activate or modify surfaces. For example, infrared radiation can be used to improve the adhesion of coatings on certain surfaces or to pre-treat plastics before painting or printing.
- Welding and joining: In process engineering, infrared radiation or laser technologies are used to weld or join materials by applying heat. This can be relevant in the plastics industry or in the manufacture of electronic components.
- Temperature measurement: Infrared thermometers are used to measure the surface temperature of materials or system components quickly and without contact. This makes it possible to monitor processes and control the temperature in real time.
The use of infrared radiation in process engineering offers advantages such as precise and controlled heat exposure, efficient energy utilization, fast process times and good adaptability to different materials and applications.