What is precipitated silicon dioxide?
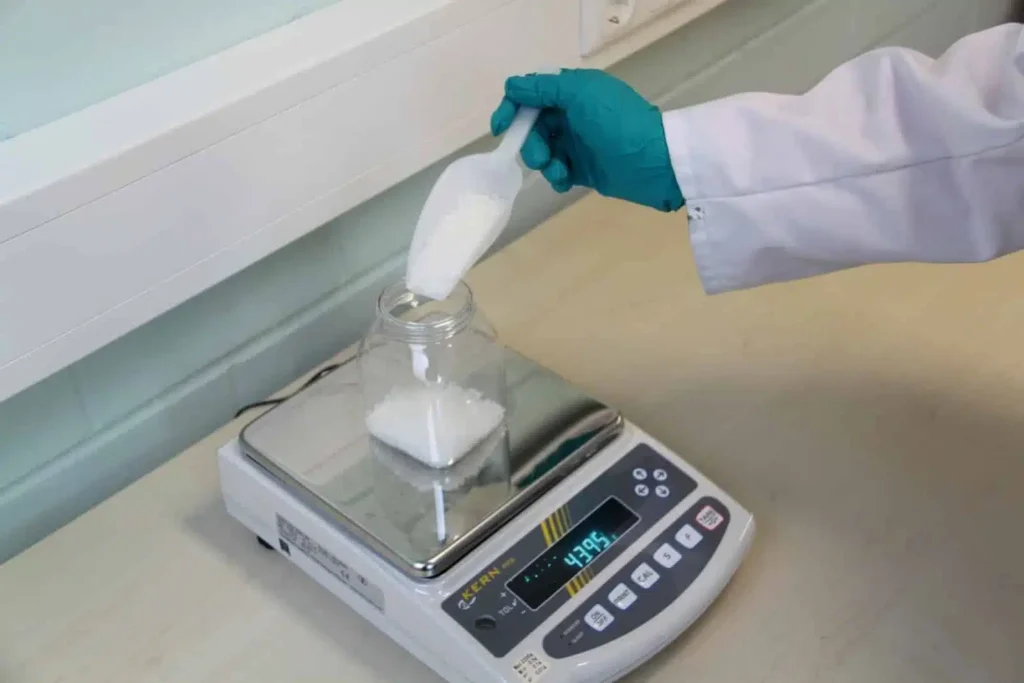
Precipitated silicon dioxide (also: precipitated silica) is an amorphous form of silicon dioxide (SiO2); it is a white, powdery material. Precipitated silica is produced by precipitation from a silicate-containing solution.
The three main classes of amorphous silica are fumed silica, precipitated silica and silica gel. Among them, precipitated silica has the greatest economic importance. In 1999, more than one million tons were produced, half of which was used in tires and shoe soles.
Precipitated silica is produced by condensing silica from a diluted alkali silicate solution, which can be obtained by dissolving quartz sand with sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate. This alkali silicate solution is also called water glass. Silica has a strong tendency to polymerize by converting silanol groups (Si-OH) into siloxane bonds (Si-O-Si). The reaction kinetics (reaction speed) is strongly dependent on the pH value.
Industrial production is carried out by acidifying an aqueous alkali silicate solution (e.g. sodium silicate) with sulphuric acid. Stirring prevents gelation, otherwise silica sols or silica gels would form.
Online source:
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gefälltes_Siliciumdioxid, retrieved: March 12, 2020, 09:20 UTC