What is viscosity? The definition
Viscosity is a unit of measurement for the viscosity of a fluid. The opposite of viscosity is fluidity (flowability). This means that the higher the viscosity, the thicker the fluid. For solids, the terms ductility, brittleness and plasticity are used instead. Occasionally toughness is used as a synonym for viscosity.
Dynamic and kinematic viscosity
The dynamic or absolute viscosity is usually determined using a rotational viscometer. In the past, viscosity was also given in poise (or centipoise). The kinematic viscosity is given inm2/sec. It is an expression for the internal friction of a liquid.
How is viscosity measured?
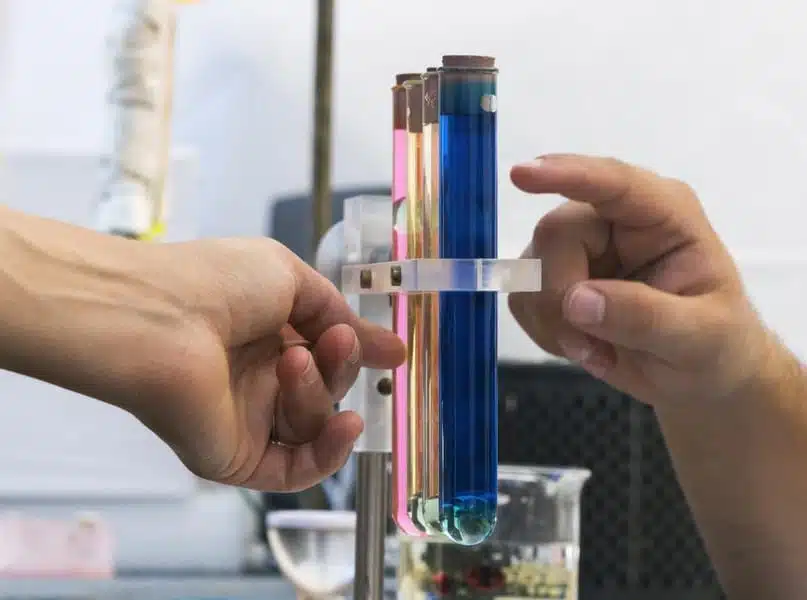
The viscosity of liquids can be measured with a viscometer. The sample to be measured is placed in the gap between two bodies in accordance with the viscosity definition. One part of the arrangement rotates or oscillates at a defined speed, while the other remains stationary. The shear rate results from the geometry of the measuring arrangement and the speed of the moving part. The torque required to maintain the movement is measured, from which the shear stress and thus the viscosity can be determined.