What does homogeneous mean?
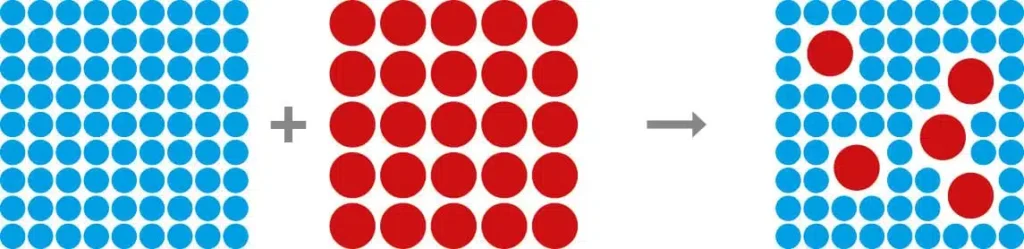
The adjective “homogeneous” describes a substance or system that is uniform and homogeneous in itself. A homogeneous system therefore consists of components that are present in the same phase and have a uniform distribution. This means that the properties, composition and density of the substance or system are the same in every part, so that there are no differences or deviations.
Homogeneous systems are found in various areas of chemistry, materials science and physics, among others, and are important in many applications.
Examples of homogeneous systems
An example of a homogeneous system is a solution in which a substance is completely dissolved in another substance. The solution is homogeneous in itself and has the same composition and density in every part:
- A salt solution in which the salt is completely dissolved in water and evenly distributed.
- Pure oxygen gas that consists of only one type of particle (oxygen atoms) and is the same in all parts of the gas.
- A clear and homogeneous solution of sugar in water in which the sugar has completely dissolved.
- A homogeneous gas mixture, such as air, which consists of different types of gases (nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc.) but is the same in all parts of the mixture.
- A homogeneous alloy in which different metals or alloying elements are evenly distributed in the metal.
- Homogenized glass in which various metal oxides are evenly dissolved in glass, resulting in a uniform color and uniform optical properties of the glass.
Homogeneous system – importance in chemistry
Homogeneity refers to the equality of a property over the entire extent of a system, or the similarity of objects, phenomena, elements of a system. In chemistry, homogeneous substances are either homogeneous mixtures, which are also called solutions, for example alloys, or pure substances. The opposite of homogeneous substances are heterogeneous substances.
Heterogeneous mixtures of substances
The opposite of homogeneous is “heterogeneous”, which means that a system consists of different parts or phases that are not evenly distributed. The term heterogeneous also comes from the Greek and means diverse, which in physics and chemistry means a system or mixture comprising several phases. The immiscible phases can be in the same aggregate state (oil and water) or different (an aqueous solution over a sparingly soluble precipitate).
Examples of heterogeneous systems
A heterogeneous system is a system in which the substances are not evenly distributed and the properties are different in different parts of the system:
- A suspension of solid particles suspended in a liquid (e.g. milk or paint). The particles are not evenly distributed and sediment if left to stand.
- A mixture of oil and water which, due to their different polarity and density, do not mix with each other and form an interface.
- A metal block with inclusions of gas bubbles, which are distributed differently and create a porous structure.
- A heterogeneous catalyst surface on which the active sites are unevenly distributed and influence the reaction rate.
- A mixture of different solids that can form a stratification due to their different size and density.
- A soil substrate with different layers and different chemical properties that influence the growth of plants.
Colloidal mixtures of substances
The individual phases are often not so easy to distinguish macroscopically. The fact that milk, for example, is a phase mixture consisting of an aqueous and a fatty phase can only be recognized under the microscope. In such cases, we speak of colloidal systems (dispersions, emulsions, aerosols), i.e. phases that are particularly finely divided in a characteristic manner.
Importance of homogeneous systems for process engineering
In chemistry and process engineering, it is often necessary to produce homogeneous systems in order to carry out chemical reactions or separate substances. One example of this is the production of solutions that must have a certain concentration of dissolved substances in order to enable certain reactions or produce materials. Another example is the production of homogeneous gas mixtures that are required for chemical reactions or analytical procedures.
In the food industry, homogeneity is important for the even distribution of ingredients and taste in products such as dairy products or sauces.